⊟Summary[edit | edit source]
- organism: Staphylococcus aureus COL
- locus tag: SACOL1437 [new locus tag: SACOL_RS07320 ]
- pan locus tag?: SAUPAN003817000
- symbol: SACOL1437
- pan gene symbol?: msaB
- synonym: cspA
- product: CSD family cold shock protein
⊟Genome View[edit | edit source]
⊟Gene[edit | edit source]
⊟General[edit | edit source]
- type: CDS
- locus tag: SACOL1437 [new locus tag: SACOL_RS07320 ]
- symbol: SACOL1437
- product: CSD family cold shock protein
- replicon: chromosome
- strand: -
- coordinates: 1449690..1449890
- length: 201
- essential: unknown other strains
⊟Accession numbers[edit | edit source]
- Gene ID: 3236557 NCBI
- RefSeq: YP_186289 NCBI
- BioCyc: see SACOL_RS07320
- MicrobesOnline: 912895 MicrobesOnline
⊟Phenotype[edit | edit source]
Share your knowledge and add information here. [edit]
⊟DNA sequence[edit | edit source]
- 1
61
121
181ATGAAACAAGGTACAGTTAAATGGTTTAACGCTGAAAAAGGATTCGGCTTTATCGAAGTT
GAAGGAGAAAATGACGTATTCGTACATTTTTCAGCAATTAACCAAGATGGTTACAAATCA
TTAGAAGAAGGTCAAGCTGTTGAGTTTGAAGTAGTTGAAGGCGACCGCGGTCCACAAGCT
GCAAACGTTGTTAAACTATAA60
120
180
201
⊟Protein[edit | edit source]
⊟General[edit | edit source]
- locus tag: SACOL1437 [new locus tag: SACOL_RS07320 ]
- symbol: SACOL1437
- description: CSD family cold shock protein
- length: 66
- theoretical pI: 4.22595
- theoretical MW: 7321.06
- GRAVY: -0.369697
⊟Function[edit | edit source]
- TIGRFAM: Cellular processes Adaptations to atypical conditions cold shock domain protein CspD (TIGR02381; HMM-score: 96.5)DNA metabolism DNA replication, recombination, and repair cold shock domain protein CspD (TIGR02381; HMM-score: 96.5)and 1 moreTranscription Degradation of RNA VacB and RNase II family 3'-5' exoribonucleases (TIGR00358; EC 3.1.13.1; HMM-score: 10.1)
- TheSEED :
- Cold shock protein of CSP family => CspA (naming convention as in S.aureus)
- PFAM: OB (CL0021) CSD; 'Cold-shock' DNA-binding domain (PF00313; HMM-score: 107.5)and 3 moreOB_RNB; Ribonuclease B OB domain (PF08206; HMM-score: 20.3)S1; S1 RNA binding domain (PF00575; HMM-score: 18.3)S1CSD-TOTE-2; S1/CSD-like domain 2 of the TOTE conflict systems (PF22707; HMM-score: 17.8)
⊟Structure, modifications & cofactors[edit | edit source]
- domains:
- modifications:
- cofactors:
- effectors:
⊟Localization[edit | edit source]
- PSORTb: Cytoplasmic
- Cytoplasmic Score: 9.97
- Cytoplasmic Membrane Score: 0
- Cellwall Score: 0.01
- Extracellular Score: 0.02
- Internal Helices: 0
- DeepLocPro: Cytoplasmic
- Cytoplasmic Score: 0.9997
- Cytoplasmic Membrane Score: 0
- Cell wall & surface Score: 0
- Extracellular Score: 0.0003
- LocateP: Intracellular
- Prediction by SwissProt Classification: Cytoplasmic
- Pathway Prediction: No pathway
- Intracellular possibility: 1
- Signal peptide possibility: -1
- N-terminally Anchored Score: 1
- Predicted Cleavage Site: No CleavageSite
- SignalP: no predicted signal peptide
- SP(Sec/SPI): 0.005783
- TAT(Tat/SPI): 0.000379
- LIPO(Sec/SPII): 0.000772
- predicted transmembrane helices (TMHMM): 0
⊟Accession numbers[edit | edit source]
⊟Protein sequence[edit | edit source]
- MKQGTVKWFNAEKGFGFIEVEGENDVFVHFSAINQDGYKSLEEGQAVEFEVVEGDRGPQAANVVKL
⊟Experimental data[edit | edit source]
- experimentally validated: PeptideAtlas
- protein localization: Cytoplasmic [1] [2] [3] [4]
- quantitative data / protein copy number per cell: 732 [5]
- interaction partners:
SACOL0452 (ahpC) alkyl hydroperoxide reductase subunit C [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2657 (arcA) arginine deiminase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0557 (cysK) cysteine synthase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1637 (dnaK) molecular chaperone DnaK [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0842 (eno) phosphopyruvate hydratase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2622 (fdaB) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1199 (ftsZ) cell division protein FtsZ [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0593 (fusA) elongation factor G [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0838 (gapA1) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1513 (hup) DNA-binding protein HU [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2623 (mqo2) malate:quinone oxidoreductase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1104 (pdhC) branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase E2 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2128 (pdp) pyrimidine-nucleoside phosphorylase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1746 (pfkA) 6-phosphofructokinase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0204 (pflB) formate acetyltransferase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1745 (pyk) pyruvate kinase [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0584 (rplA) 50S ribosomal protein L1 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2236 (rplB) 50S ribosomal protein L2 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2239 (rplC) 50S ribosomal protein L3 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2238 (rplD) 50S ribosomal protein L4 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2227 (rplE) 50S ribosomal protein L5 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2224 (rplF) 50S ribosomal protein L6 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0585 (rplJ) 50S ribosomal protein L10 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0583 (rplK) 50S ribosomal protein L11 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0586 (rplL) 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2207 (rplM) 50S ribosomal protein L13 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2220 (rplO) 50S ribosomal protein L15 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1257 (rplS) 50S ribosomal protein L19 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1702 (rplU) 50S ribosomal protein L21 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2234 (rplV) 50S ribosomal protein L22 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2237 (rplW) 50S ribosomal protein L23 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0588 (rpoB) DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0589 (rpoC) DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta' [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1769 (rpsD) 30S ribosomal protein S4 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2222 (rpsE) 30S ribosomal protein S5 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2206 (rpsI) 30S ribosomal protein S9 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2214 (rpsK) 30S ribosomal protein S11 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2230 (rpsQ) 30S ribosomal protein S17 [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0095 (spa) immunoglobulin G binding protein A precursor [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0541 (spoVG) regulatory protein SpoVG [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1722 (tig) trigger factor [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1276 (tsf) elongation factor Ts [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0594 (tuf) elongation factor Tu [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL0731 LysR family transcriptional regulator [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1753 universal stress protein [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL1759 universal stress protein [6] (data from MRSA252) SACOL2173 alkaline shock protein 23 [6] (data from MRSA252)
⊟Expression & Regulation[edit | edit source]
⊟Operon[edit | edit source]
- MicrobesOnline: no polycistronic organisation predicted
⊟Regulation[edit | edit source]
- regulator:
⊟Transcription pattern[edit | edit source]
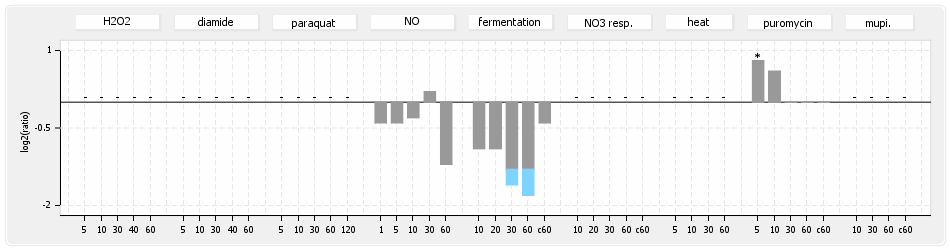
- S.aureus Expression Data Browser: data available for NCTC8325
⊟Protein synthesis (provided by Aureolib)[edit | edit source]
⊟Protein stability[edit | edit source]
- half-life: 28.6 h [7]
⊟Biological Material[edit | edit source]
⊟Mutants[edit | edit source]
⊟Expression vector[edit | edit source]
⊟lacZ fusion[edit | edit source]
⊟GFP fusion[edit | edit source]
⊟two-hybrid system[edit | edit source]
⊟FLAG-tag construct[edit | edit source]
⊟Antibody[edit | edit source]
⊟Other Information[edit | edit source]
You can add further information about the gene and protein here. [edit]
⊟Literature[edit | edit source]
⊟References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Dörte Becher, Kristina Hempel, Susanne Sievers, Daniela Zühlke, Jan Pané-Farré, Andreas Otto, Stephan Fuchs, Dirk Albrecht, Jörg Bernhardt, Susanne Engelmann, Uwe Völker, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker
A proteomic view of an important human pathogen--towards the quantification of the entire Staphylococcus aureus proteome.
PLoS One: 2009, 4(12);e8176
[PubMed:19997597] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I e) - ↑ Kristina Hempel, Jan Pané-Farré, Andreas Otto, Susanne Sievers, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
Quantitative cell surface proteome profiling for SigB-dependent protein expression in the human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus via biotinylation approach.
J Proteome Res: 2010, 9(3);1579-90
[PubMed:20108986] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I p) - ↑ Kristina Hempel, Florian-Alexander Herbst, Martin Moche, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
Quantitative proteomic view on secreted, cell surface-associated, and cytoplasmic proteins of the methicillin-resistant human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus under iron-limited conditions.
J Proteome Res: 2011, 10(4);1657-66
[PubMed:21323324] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I p) - ↑ Andreas Otto, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
The Staphylococcus aureus proteome.
Int J Med Microbiol: 2014, 304(2);110-20
[PubMed:24439828] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I p) - ↑ Daniela Zühlke, Kirsten Dörries, Jörg Bernhardt, Sandra Maaß, Jan Muntel, Volkmar Liebscher, Jan Pané-Farré, Katharina Riedel, Michael Lalk, Uwe Völker, Susanne Engelmann, Dörte Becher, Stephan Fuchs, Michael Hecker
Costs of life - Dynamics of the protein inventory of Staphylococcus aureus during anaerobiosis.
Sci Rep: 2016, 6;28172
[PubMed:27344979] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I e) - ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 6.20 6.21 6.22 6.23 6.24 6.25 6.26 6.27 6.28 6.29 6.30 6.31 6.32 6.33 6.34 6.35 6.36 6.37 6.38 6.39 6.40 6.41 6.42 6.43 6.44 6.45 6.46 Artem Cherkasov, Michael Hsing, Roya Zoraghi, Leonard J Foster, Raymond H See, Nikolay Stoynov, Jihong Jiang, Sukhbir Kaur, Tian Lian, Linda Jackson, Huansheng Gong, Rick Swayze, Emily Amandoron, Farhad Hormozdiari, Phuong Dao, Cenk Sahinalp, Osvaldo Santos-Filho, Peter Axerio-Cilies, Kendall Byler, William R McMaster, Robert C Brunham, B Brett Finlay, Neil E Reiner
Mapping the protein interaction network in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
J Proteome Res: 2011, 10(3);1139-50
[PubMed:21166474] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I p) - ↑ Stephan Michalik, Jörg Bernhardt, Andreas Otto, Martin Moche, Dörte Becher, Hanna Meyer, Michael Lalk, Claudia Schurmann, Rabea Schlüter, Holger Kock, Ulf Gerth, Michael Hecker
Life and death of proteins: a case study of glucose-starved Staphylococcus aureus.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2012, 11(9);558-70
[PubMed:22556279] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (I p)
⊟Relevant publications[edit | edit source]
H De Lencastre, S W Wu, M G Pinho, A M Ludovice, S Filipe, S Gardete, R Sobral, S Gill, M Chung, A Tomasz
Antibiotic resistance as a stress response: complete sequencing of a large number of chromosomal loci in Staphylococcus aureus strain COL that impact on the expression of resistance to methicillin.
Microb Drug Resist: 1999, 5(3);163-75
[PubMed:10566865] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (P p)Samuel Katzif, Damien Danavall, Samera Bowers, Jacqueline T Balthazar, William M Shafer
The major cold shock gene, cspA, is involved in the susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to an antimicrobial peptide of human cathepsin G.
Infect Immun: 2003, 71(8);4304-12
[PubMed:12874306] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (P p)Samuel Katzif, Eun-Hee Lee, Anthony B Law, Yih-Ling Tzeng, William M Shafer
CspA regulates pigment production in Staphylococcus aureus through a SigB-dependent mechanism.
J Bacteriol: 2005, 187(23);8181-4
[PubMed:16291691] [WorldCat.org] [DOI] (P p)